Recombinant Proteins
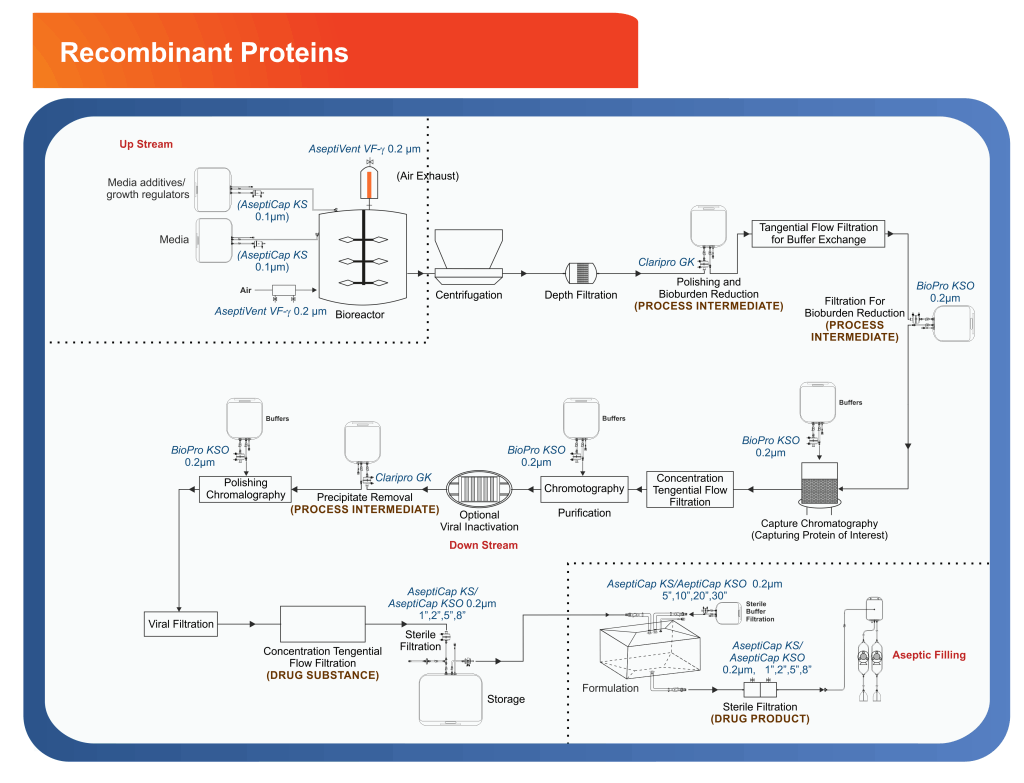
Proteins that result from the expression of recombinant DNA within living cells are termed recombinant proteins. The majority of therapeutic proteins are recombinant human proteins manufactured using non-human mammalian cell lines that are engineered to express certain human genetic sequences to produce specific proteins.
Recombinant proteins are an important class of therapeutics used to replace deficiencies in critical blood borne growth factors and to strengthen the immune system to fight cancer and infectious diseases. The growth in the use of recombinant proteins has increased greatly in recent years. By putting specific genes into the genetic material of bacteria, mammalian or yeast cells, these microorganisms or cells can be used as factories or producers to make proteins for medical treatment and diagnostics.
Flowchart: You can go to the product page by clicking on the product name shown in the flowchart